Tutorial on using the distillation and loss operationsExample - model of ethanol production by fermentation using this flowchart editor / process simulator
Before you continue......you should have a basic understanding of the following:Topic and recipe of example projectProduce ethanol from sugar by fermentation Dissolve 30 kg of sugar in 100 litres of aqueous 2.9 g/l sodium citrate buffer solution. Add some fermentation culture to it and let the formed CO2 leave into the air. Then distill off the formed ethanol from the mixture. Tip: try to follow this tutorial with the flowchart editor using example project: Ethanol production by fermentation! Chemical reactions: transformation of compoundsThe main point of the operation "reaction" is to define transformation of compounds. Chemical reactions, microbiological transformations - these are the same. One point is common: the principle of mass conservation must be satisfied, i.e. as many mass reacts ("disappears" from the system) so many mass must form ("appear" in the system). The program forces it consequently. Note: this program version does not requires total knowledge about reaction mechanisms as well as it does not requires the chemical equations coefficients. Even complex reaction systems can be handled either "careless" or precise. The main point is the mass balance. Reactants and products should be defined this way:
Let's see an example (as in the title): Produce ethanol from sugar by fermentation. 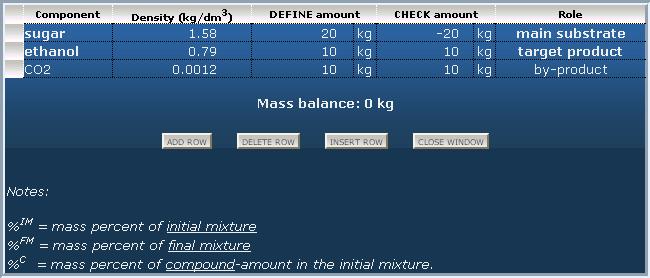
Another example: Produce the sodium citrate mentioned in the recipe by reaction of sodium hydrogen carbonate and citric acid. 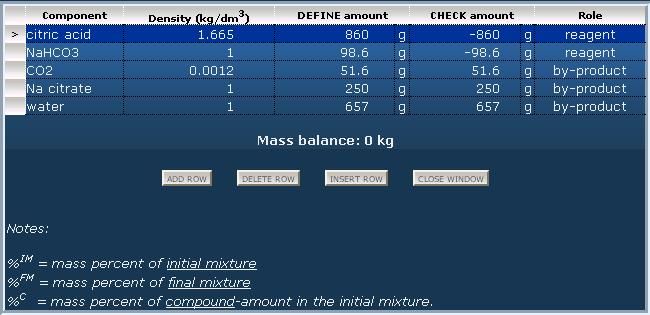
Loss by reactions: handling of gaseous compoundsThere are reactions where gaseous compounds form (in our example carbon dioxid), and there are reactions where gaseous reagents are used (e.g. hydrogenation). Excess gaseous reagents and useless gaseous by-products may be released out into the air, and for this kind of loss can be used the "loss" operation. Before this an output material must be definied for summarizing losses (e.g. "lost compounds into the air" or "exhaust gases into the air"). 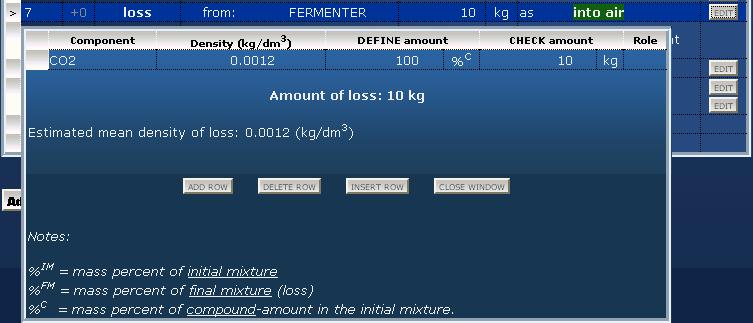
Another solution is the absorption of the formed gases in an absorber equipment. (e.g. the formed hidrochloric acid gas is conducted to dilute sodium hydroxide solution.) Page top Home |
Useful tools
Chemical Equations Balancer
Solving of chemical equations, automatic determination of stochiometric coefficients.
Chemical Equations Balancer
Solving of chemical equations, automatic determination of stochiometric coefficients. |
process-flow-diagram.com -- generate chemical technological flowsheets based on material flow calculations
Privacy policy Last update:

