Tutorial on using the filtration operationExample - how to model clarification, crystallization and filtration with this flowchart editor / process simulator
Before you continue......you should have a basic understanding of the following:Topic and recipe of example projectPurify sugar from it's impurities by clarification with activated carbon, and crystallization according to the following recipe: Dissolve 80 kg crude sugar in 100 litres of water (on about 90°C), and clarify it with 5 kg of activated carbon. Then filter off the hot mixture. Cool down the filtrate (crystallization begins) and add 50 litres of ethanol to it (more sugar precipitates because of the weaker solubility in alcohol). Then filter the sugar crystals, and wash the filter cake with 10 litres ethanol. Tip: try to follow this tutorial with the flowchart editor using example project: Sugar crystallization! Clarification: mix some clarifying material with the liquid and then separate itSince the program handles the actual content of a vessel as a homogenous mixture (in other words: the program does not distinguish solid and liquid components), "clarification" means "load clarifying material and then filter it off".1st type of filtration: separate insoluble solids from liquid Follow these principles during definition of component separation:
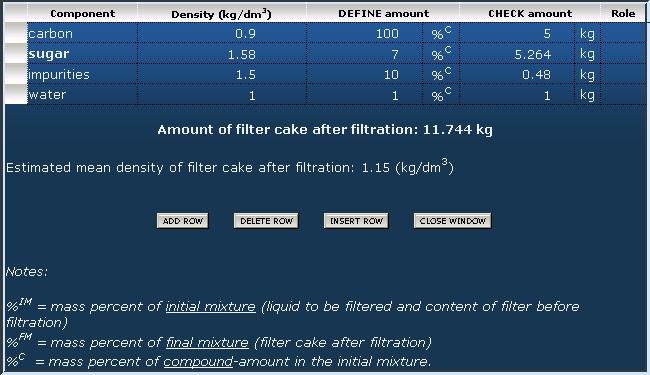
Some explanations of the component amounts in this example:
Use the same principles. Nothing else. Crystallization: separation of precipitated material from the solutionSince the program handles the actual content of a vessel as a homogenous mixture (in other words: the program does not distinguish solid and liquid components), "crystallization" does not have it's own "operation code". The user should keep in mind which components are solid and which are liquid or dissolved, and use this information when these solids are filtered.2nd type of filtration: separate soluble solids from liquid Follow these principles during definition of component separation:
Page top Home |
Useful tools
Filtration Calculations
Filtration Calculations: cake resistance, filtration time, pressure drop, etc.
Filtration Calculations
Filtration Calculations: cake resistance, filtration time, pressure drop, etc. |
process-flow-diagram.com -- generate chemical technological flowsheets based on material flow calculations
Privacy policy Last update:

